Capacity planning
Capacity planning involves calculating the capacity needed to achieve the priority plan and finding ways of making that capacity available. If the capacity required cannot be met, the priority plans have to be changed.
Priority plans are usually stated in units of product or some standard unit of output. Capacity can sometimes be stated in the same units. If there is no common unit, capacity must be stated as the hours available. The process of capacity planning is as follows:
- Determine the capacity available at each work center in each time period;
- Determine the load at each work center in each time period:
o Translate the priority plan into the hours of work required at each work center in each period time,
o Sum up the capacities required for each item on each work center to determine the load on each work center in each time period;
- Resolve differences between available capacity and required capacity.
Capacity planning is executed at four levels: resource planning, rough-cut capacity planning, capacity requirements planning, and input/output control.
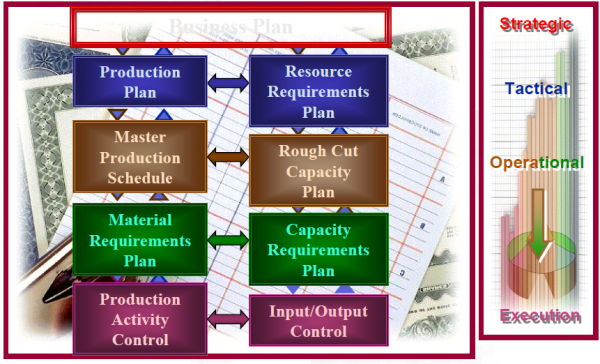
Resource planning involves long-range capacity resources requirements and is directly linked to production planning. Typically , it involves translating monthly, quarterly or annual product priorities from the production plan into some total measure of capacity, such as gross labor hours. Resource planning involves changes in manpower, capital equipment, product design or other facilities that take a long time to acquire and eliminate.
What is RCCP?
A problem commonly encountered in operating MRP systems is the existence of an overstated MPS. An overstated master production schedule is one that orders more production to be released than production can complete. An overstated MPS causes raw materials and WIP inventories to increase because more materials are purchased and released to the shop than are completed and shipped. It also causes a buildup of queues on the shop floor. Since jobs have to wait to be processed, actual lead times increase, causing ship dates to be missed. As lead times increase, forecast accuracy over the lead-time diminishes because forecasts are more accurate for shorter periods than for longer ones. Thus, overstated master production schedules lead to missed due dates and other problems. Validating the MPS with respect to capacity is an extremely important step in MRP. This validation exercise has been termed rough cut capacity planning (RCCP).
What is CRP
You can use CRP to verify that you have sufficient capacity available to meet the capacity requirements for your MRP plans. In this way, you can identify short term discrepancies between required and available capacity.
CRP typically verifies capacity for all the resources required to meet your material plan.
The various capacity plans relate only to their level in the priority plan, not to subsequent capacity planning levels.After the plans are completed, production activity control and purchasing must be authorized to process or implement shop orders and purchase orders.