Production Scheduling
Scheduling is an important tool for manufacturing and engineering, where it can have a major impact on the productivity of a process. In manufacturing, the purpose of scheduling is to minimize the production time and costs, by telling a production facility when to make, with which staff, and on which equipment. Production scheduling aims to maximize the efficiency of the operation and reduce costs.
Production scheduling tools greatly outperform older manual scheduling methods. These provide the production scheduler with powerful graphical interfaces which can be used to visually optimize real-time work loads in various stages of production, and pattern recognition allows the software to automatically create scheduling opportunities which might not be apparent without this view into the data. For example, an airline might wish to minimize the number of airport gates required for its aircraft, in order to reduce costs, and scheduling software can allow the planners to see how this can be done, by analyzing time tables, aircraft usage, or the flow of passengers.
Companies use backward and forward scheduling to allocate plant and machinery resources, plan human resources, plan production processes and purchase materials.
Forward scheduling is planning the tasks from the date resources become available to determine the shipping date or the due date.
Backward scheduling is planning the tasks from the due date or required-by date to determine the start date and/or any changes in capacity required.
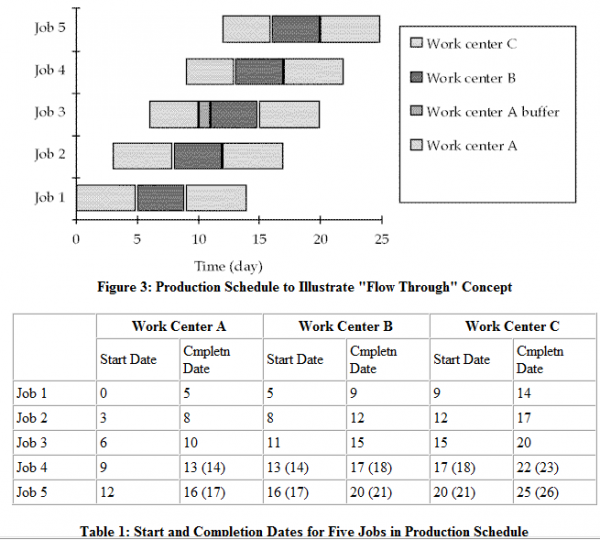
Back scheduling The usual process is to start with the due date and using the lead times to work back to find the start date for each operation. This process is called back scheduling. To schedule, we need to know for each order:
- The quantity and due date;
- Sequence of operations and work centers needed;
- Setup and run times for each operation;
- Queue, wait and move times;
- Work center capacity available (rated or demonstrated),
The information needed is obtained from the following:
- Order file. Quantities and due dates;
- Route file. Sequence of operations, work centers needed, setup time and run time;
- Work center file. Queue, move and wait times and work center capacity.
The process is as follows:
- For each work order, calculate the capacity required (time) at each work center;
- Starting with the due date, schedule back to get the completion and start dates for each operation.